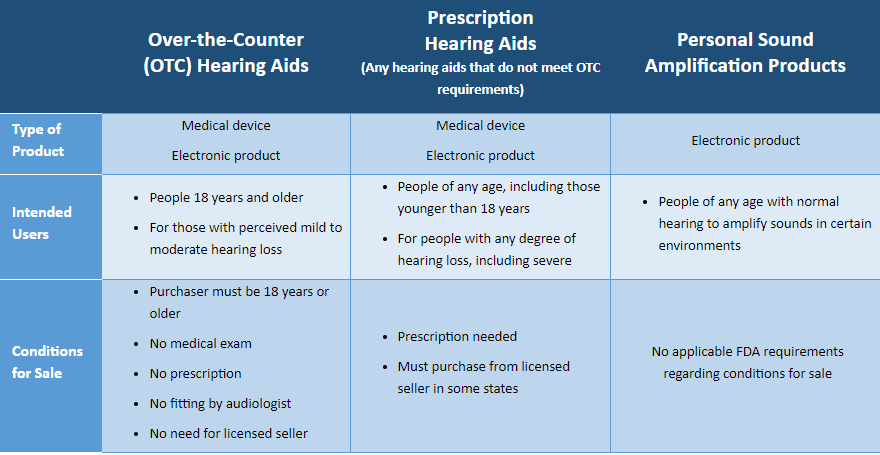
More than 38 million American adults have some form of hearing difficulty. To overcome barriers and increase access to hearing assistance, a new category of hearing aids known as Over the Counter (OTC) hearing aids became effective in October 2022 allowing consumers an additional option for addressing their hearing health. OTC hearing aids are intended for use by adults (age 18 or over) with perceived mild to moderate hearing loss.
Hearing aids, like any other medical device, should be carefully considered before making a selection. While not required, a visit to a licensed hearing professional to know the details of your hearing loss is the best first step to finding the right treatment option. A hearing professional, such as an audiologist, hearing instrument specialist, or ENT physician (ear, nose, and throat doctor), can test your hearing, help you understand your unique type of hearing loss, and determine the best course of treatment that fits your lifestyle and long-term needs.
Hearing aids are medical devices and are regulated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to ensure safety and efficacy for consumers. There are two categories of hearing aids:
Personal sound amplification products (PSAPs) are not hearing aids and are not regulated as medical devices or by the FDA. PSAPs are intended for non-hearing-impaired individuals to amplify sounds in certain environments, such as for hunting or other recreational activities, and are not intended to treat hearing loss. Check the packaging closely. PSAPs may go by names such as “hearing amplifier”, “sound amplifier”, “sound enhancer”.
Hearing loss is unique to each individual and, in support of best practice, it is advisable to see a hearing professional to understand your individual hearing loss prior to making a purchase whether OTC or prescription. Seek help from a hearing healthcare professional if you can’t hear speech even if the room is quiet or if you don’t hear loud sounds well. See a doctor if you experience any “red flag” conditions. Red flag conditions include birth defects or deformed ears following an accident; presence of blood, pus, or fluid coming out of your ear in the past 6 months; ear pain or discomfort; excessive earwax or you think something could be in your ear; dizziness, spinning, or swaying (vertigo); sudden change in hearing in the past 6 months; changes in hearing, such as getting worse and then better; worse hearing in one ear; or ringing or buzzing in only one ear.
If you’re searching for an OTC hearing aid, be sure to follow these tips:
To check the FDA database of listed devices and registered companies, click here.
You may have seen words like this on a website, tv advertisement, or other ad selling hearing aids in the United States, sometimes even with an FDA logo:
Beware of advertising that contains these words, as they may be used to mislead you. Owners or operators of places of business that are involved in the production and distribution of medical devices intended for use in the United States are generally required to register annually with the FDA. However, this registration does not denote approval, clearance, or authorization of that facility or its medical devices. FDA does not issue any type of device registration certificates to medical device facilities and does not “certify” registration information for businesses that have registered and listed. A manufacturer must “register” its establishment and “list” its devices, but this does not necessarily mean FDA has specifically approved or cleared that device. To search for establishment registrations and device listings, visit the FDA’s Establishment Registration & Device Listing database. Additionally, the FDA logo is for official government use only. The FDA logo should not be used to misrepresent the agency or to suggest that the FDA endorses any private organization, product, or service.
OTC hearing aids must be listed with the FDA and follow applicable regulations. Self-fitting hearing aids, which allow for greater customization, must satisfy premarket notification requirements and special controls. Any OTC hearing aid sold that claims to be self-fitting OTC should have been reviewed by FDA. If a manufacturer advertises “self-fitting OTC hearing aids,” they must be listed under the appropriate product code in the FDA database, indicating that those devices have obtained FDA clearance. Beware of any claims that a hearing aid will fix your hearing loss, restore normal hearing, or broad claims that the device is better than more expensive products.
The following resource may help you learn more about hearing loss, hearing aids, and how to find a hearing healthcare professional. Hearing health professionals are licensed by the individual states and subject to state training standards, which do not apply when obtaining a hearing aid from a retailer. Additional hearing health information, directories, and screening tools are provided at the following link: https://www.hearing.org/find-a-hearing-professional/
Learn more about the history of the Over-the-Counter Hearing Aid Act and frequently asked questions: https://betterhearing.org/policy-research/otc-hearing-aids/
To report a problem involving your hearing aid, you should submit information to FDA as soon as possible after the problem occurs. FDA encourages consumers and professionals to file any adverse events related to the use of OTC hearing aids, not limited to significant injury and/or death. Additional adverse events may include irritation of the ear canal or outer ear skin, injury from the device (like cuts or scratches, or burns from an overheated battery), pieces of the device getting lodged in the ear canal, or sudden increased severity in hearing loss with the device.
Instructions for reporting are available at https://www.fda.gov/Safety/MedWatch, or call 1-800-FDA-1088. You can also download a form to mail to FDA.